The H5N1 strain of avian influenza, also known as bird flu, has emerged as a significant public health concern due to its potential to cause severe illness in humans. Understanding the complexities of H5N1 bird flu, including its symptoms, transmission, and public health implications, is crucial for effective prevention and response strategies.
Symptoms of H5N1 Bird Flu
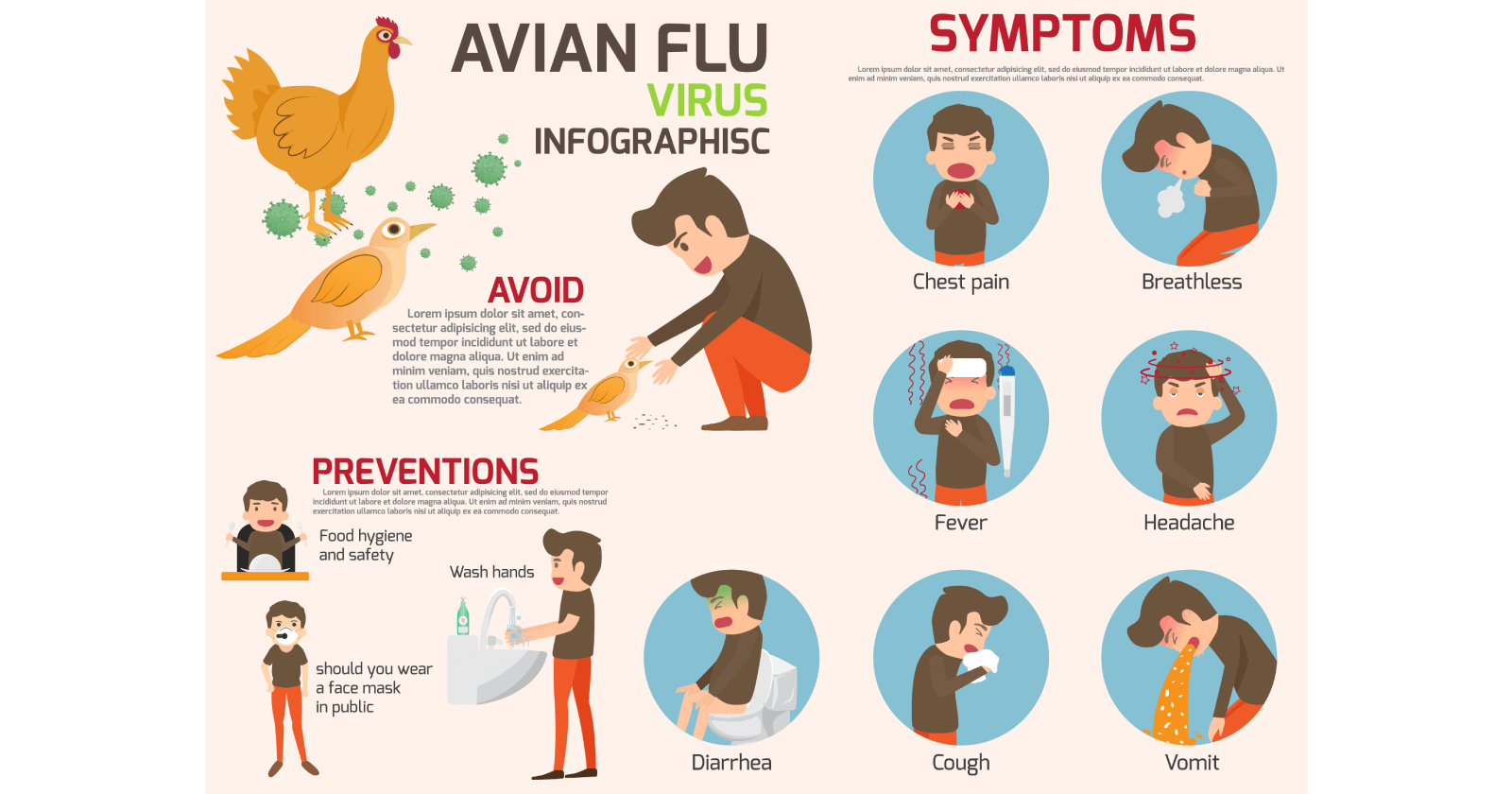
The symptoms of H5N1 bird flu in humans can vary depending on the severity of the infection. Mild cases may present with flu-like symptoms such as:
- Fever
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Muscle aches
- Headache
However, in severe cases, H5N1 bird flu can lead to serious respiratory complications, including:
- Pneumonia
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- Multi-organ failure
The fatality rate for H5N1 bird flu in humans is estimated to be around 60%, making it a highly virulent strain.
Transmission of H5N1 Bird Flu
H5N1 bird flu is primarily transmitted from birds to humans through direct or indirect contact with infected birds or their bodily fluids. The following are the main routes of transmission:
- Direct contact: Handling live or dead infected birds, or contact with their saliva, nasal secretions, or feces.
- Indirect contact: Touching contaminated surfaces or objects, such as poultry products, feathers, or cages.
- Inhalation: Inhaling respiratory droplets from infected birds or contaminated environments.
Human-to-human transmission of H5N1 bird flu is also possible but is considered rare. It has been reported in cases of close contact with an infected person, such as family members or healthcare workers.
Public Health Concerns
The emergence of H5N1 bird flu in humans raises significant public health concerns:
- Pandemic potential: H5N1 bird flu has a high mutation rate, making it capable of adapting to new hosts and potentially causing a pandemic.
- Severity of illness: The high fatality rate associated with H5N1 bird flu poses a serious threat to human health.
- Lack of effective treatment: Currently, there is no specific treatment for H5N1 bird flu, and antiviral medications may not be effective in all cases.
Prevention and Control
Preventing and controlling the spread of H5N1 bird flu requires a comprehensive approach involving:
- Surveillance and monitoring: Regular monitoring of poultry populations and humans for signs of infection.
- Biosecurity measures: Implementing strict biosecurity measures on poultry farms and other locations where birds are kept.
- Vaccination: Vaccinating poultry against H5N1 bird flu to reduce the risk of infection in animals and humans.
- Public health education: Raising awareness about the risks of bird flu and promoting hygiene practices.
- Stockpiling of antiviral medications: Building up a stockpile of antiviral medications for use in the event of an outbreak.
Conclusion
H5N1 bird flu is a complex and evolving public health challenge. Its potential to cause severe illness and its pandemic potential warrant ongoing surveillance, research, and preventive measures. By understanding the symptoms, transmission, and public health implications of H5N1 bird flu, we can develop effective strategies to protect human health and mitigate the risk of a global pandemic.
